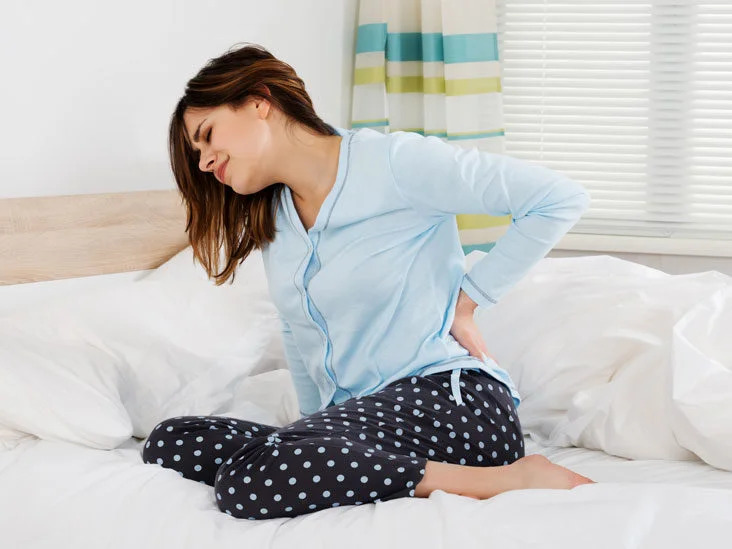
Bacterial infection of the bladder is the main cause of bladder infections. Another name for it is a urinary infection. Urging frequently, burning while peeing, soreness, and other symptoms can all be signs of a bladder infection. In individuals with compromised immune systems, yeast can also be a factor in UTIs.
Cystitis is the name for bladder irritation brought on by bacterial infection. Bladder problems typically have abrupt, unexpected symptoms. On the other hand, certain cases could be chronic, meaning they persist for a long time. More women than men are typically affected by bladder infections. Treating urinary infections early on is essential to stopping the illness from spreading.
Bladder infection V/s urinary tract infections
Urinary tract infections are another term for bladder infections. Anywhere in the urinary tract, including the kidneys, bladder, ureter, and urethra, can become infected with this infection. Kidneys and ureters are parts of the upper urinary tract. Urine is produced by the kidneys after blood is filtered to remove contaminants. While the urine is transported to the lower tract via the ureter. The lower urinary tract includes the urethra and bladder. Urine is kept in reserve within your bladder until you let it out. The urethra is where pee leaves the body. Because it is easier for bacteria to access the lower tract, urinary infections typically arise there.
Causes of bladder infection
When bacteria enter the body through the urethra and proceed in the direction of the bladder, they can cause illness. Usually, the body attempts to get rid of the bacteria by peeing them out of the body. On sometimes, bacteria may attach themselves to the bladder wall and grow quickly. This makes it difficult for the body to eliminate them, which might result in a bladder infection. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a major cause of bladder infections. The big intestine is home to these bacteria by nature. Bacteria from stool can potentially cause an illness by entering your body through the urethra and getting on your skin. Because the female urethra is tiny and its external opening is close to the anus, bacteria from the stool can easily enter the Urinary tract.
Symptoms
Depending on the severity of the bladder infection, several symptoms can be experienced. The following are a few of the most typical signs of a bladder infection:
Urinating with pain or burning
murky or bleeding pee
urinating more often than usual—a condition known as frequency
a persistent need to urinate—a condition known as “urgency.”
Urine with an offensive odor
a pressure-like cramping sensation in your lower back or abdomen.
Back pain in the middle can result from the progression of bladder infections. The kidney infection is the cause of this pain. It won’t go away no matter how you stand or what you do.
Kidney infection will result in:
fever.Feels cold.queasy feeling.throwing up
Kidney infections necessitate medical attention since they are more serious than bladder infections. For more information, speak with your doctor. You can experience additional symptoms of a urinary infection. Although bladder infections are prevalent, men and women are at distinct risk.
Bladder infections in women
Infections of the bladder are more prevalent in women. In the United States, 40% of women have experienced a urinary tract infection at some point in their lives. This is because women’s urethras are shorter, which allows bacteria to more easily enter the bladder. Because of its closer proximity to the urethra, a woman’s rectum is more prone to infections. Due to changes in the urinary tract, there is an increased risk of bladder infection during pregnancy. Bladder infections are also more common as a result of immune system modifications. The use of blood contraceptives, such as spermicides and diaphragms, may raise your risk of UTIs. Because they are more likely to recur, about 25% of women contract the same infection six months after initially contracting it.infections.
Bladder infections in men
Men over 65 are more likely than women to get bladder infections. But younger, uncircumcised men who indulge in anal intercourse could be seriously harmed. Both men and women are more susceptible to bladder infections due to a number of additional reasons. They are listed in the following order:
advanced age
Motionlessness
inadequate consumption of fluids
A urinary catheter A urinary tract surgical operation
Diabetes Illness to the immune system
leaking of stools
bladder-related neurodegeneration, such as multiple sclerosis
Urinary retention is the term for trouble passing urine.
Diagnosis
A urinalysis is a simple way to diagnose bladder infections. White blood cells, red blood cells, nitrites, and bacteria in the urine are all removed during this test.
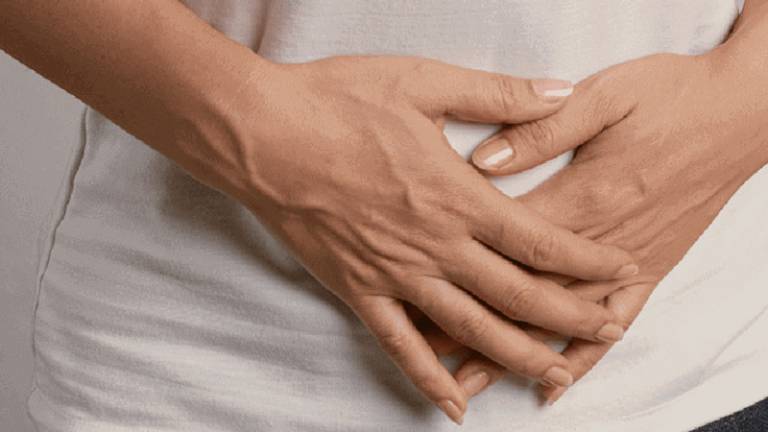

Bladder infection treatment
Treatment for bladder infections is required to get rid of bacteria and the problems they cause. Medication is used to treat pain, burning, and other symptoms of a urinary tract infection, while antibiotics are provided to eradicate the bacteria causing the bladder infection. Additionally, bladder cancer treatment varies. Regarding drugs for bladder cancer, speak with a medical professional.
Medication for urinary infections: Doctors give oral antibiotics to treat bladder infections and eradicate bacteria, as well as pain and burning sensations.
Home treatment – along with the medications, there are precautionary steps to take to treat your infection:
- It is helpful to flush out the germs in your bladder by drinking lots of water or other fluids. Because it doesn’t include artificial sweeteners or caffeine, which might irritate the bladder, water is the best beverage.
- Juices, extracts, and preparations made from concentrated cranberries may aid in infection prevention, but they shouldn’t be the only course of treatment for an existing infection.
- Urinating both before and after intercourse reduces the risk of infection.