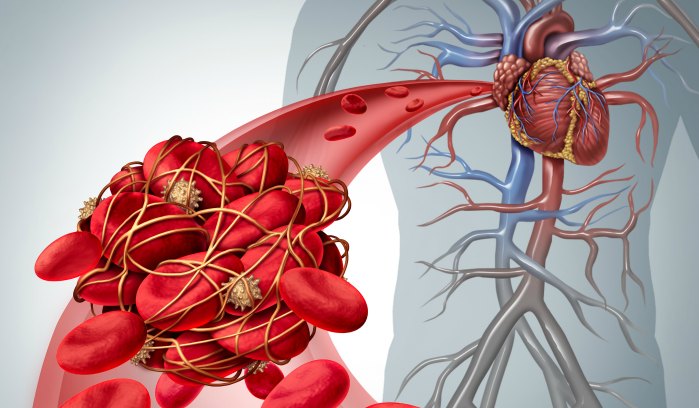
Blood clots in veins, pulmonary embolisms (blood clots in the lungs), and arterial thrombosis (blood clot in the artery) are all treated and prevented with anticoagulant medications, which are categorized as blood thinners.
Anticoagulants Vs Blood thinner
It’s critical to realize that anticoagulants are just blood thinners when discussing anticoagulants vs blood thinners. Blood thinners primarily come in two varieties: anticoagulants and antiplatelets.
Anticoagulants, such as Warfarin or Heparin, slow down your body’s ability to form clots. Antiplatelets, such as clopidogrel and aspirin, stop platelets from aggregating to create a clot. Patients who have experienced a heart attack or stroke are prescribed antiplatelet medications.
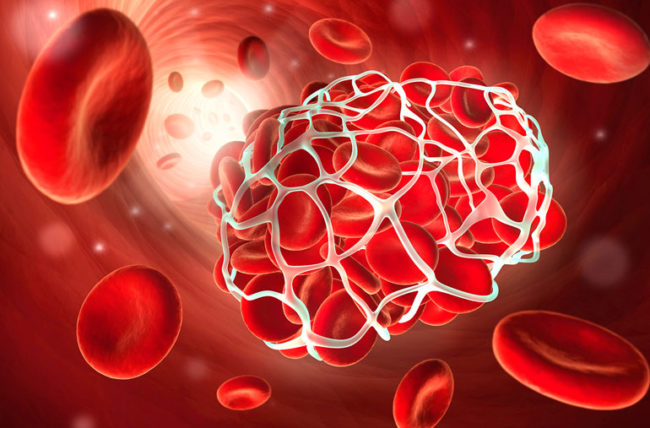
Why would I need to take anticoagulants?
Blood clots can be quite harmful when they develop in the circulation. Large clots have the potential to lodge in tiny blood vessels. Should that smaller blood artery exist. One of your body organs’ essential blood circulation may be restricted if the smaller blood vessel is situated in a dangerous area. Blood clot-related blockages can result in the following potentially fatal issues:
A pulmonary embolism happens when a blood clot lodges in an artery in the lung, obstructing it. This disorder can be fatal if the obstruction is severe enough.
Stroke: Blood clots can readily become lodged in the tiny blood veins in the brain, making them very fatal if they travel that high.
A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, happens when an artery supplying blood to the heart becomes blocked. These obstructives may potentially be fatal.
- A pulmonary embolism happens when a blood clot lodges in an artery in the lung, obstructing it. This disorder can be fatal if the obstruction is severe enough.
- Stroke: Blood clots can readily become lodged in the tiny blood veins in the brain, making them very fatal if they travel that high.
- A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction, happens when an artery supplying blood to the heart becomes blocked. These obstructives may potentially be fatal.
Anticoagulants impede blood clotting; they are also referred to as blood thinners. Commonly used medications include apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, heparin, and warfarin. It is more difficult for blood clots to develop in your veins, arteries, and heart when you take these blood thinners. They also prevent blood clots that already present from getting bigger. Be the Make careful to adhere to these guidelines when taking an anticoagulant medication:
- Adhere to the doctor’s prescription for blood thinners exactly.
- It is crucial to have routine blood tests if you use Warfarin so your healthcare provider can explain how it functions.
- Before using aspirin with anticoagulant medication, wait to hear from your doctor.
- Ensure that your doctor is aware of the anticoagulant drugs you are taking.
- Consult your physician prior to beginning any new supplement or medication regimen. This includes over-the-counter medications, antibiotics, aspirin, vitamins, cold remedies, and sleeping aids. These may strengthen or weaken anticoagulant medications, affecting how they function.
- Talk to your health care provider about your nutrition. Vitamin K-containing foods may lessen Warfarin’s efficacy. Vegetable oils, lentils, soybeans, and green leafy vegetables are good sources of vitamin K.
How do they work?
The balance between clotting and anti-clotting mechanisms is a continuous task for your body. If your blood doesn’t clot sufficiently after an injury, you could lose a lot of blood or possibly die. Deadly events can potentially result from excessive clotting. An inert clotting process can be attributed to specific components present in the blood. In this manner, in the event of an injury that requires healing, your body will be able to quickly activate them. Because of this delicate balancing effort, clotting is typically a beneficial process. It halts bleeding, creates a barrier to keep bacteria out of a wound, and then the skin regenerates. Anticoagulants work by obstructing the body’s natural clotting mechanisms. They stop your blood from solidifying into a clot, a process known as coagulation.
Oral medications
Warfarin: A vitamin K antagonist, Warfarin prevents the body from using vitamin K, which is essential to the clotting process. The fact that this blood clotting drug requires cautious dosage and frequent testing, as prescribed by the physician, is a significant drawback. A dose that is too high could cause severe hemorrhage. Only Warfarin is prescribed in specific circumstances. These include diseases affecting the mitral valve in your heart, end-stage kidney disease, and mechanical heart valves.
Anticoagulants directly
The Food and Drug Administration has also approved dabigatran, edoxaban, apixaban, and betrixaban as anticoagulants in recent years. Without routine lab testing, these blood clotting drugs can be administered on a regular basis. When taking Warfarin is not an option, they are frequently given. You might not need to get your clotting checked when using these. These drugs block a specific clotting factor right away. In just a few hours, they start to work. Pregnant and nursing women shouldn’t use anticoagulants because there isn’t enough information on their use in these situations.
Could anticoagulant medicines cause a problem?
The adverse effects of blood thinners should be known to you. You should not experience any issues if you adhere to your doctor’s advice. But you immediately inform them if:
You believe you are expecting a child or are pregnant.
It looks like your pee is brown, red, or pink. This may indicate bleeding in the urinary tract.
Your stools seem to be either black, dark brown, or crimson. This may be a sign of bleeding inside the intestine.
When you get your period, you bleed more heavily than usual.
Your gums are bleeding.
You’re experiencing a severe headache or persistent stomach pain.
You frequently get blood blisters or bruises.
You feel faint, weak, or dizzy, or you become nauseous.
You experience an incident, like a head bump or an open wound that is not stopping.
Conclusion
Cardiovascular disease, stroke, and pulmonary embolism are among the fatalities that anticoagulants save. Additionally, there are many ways in which these medications work within the body. In this manner, those who are unable to take one medication may still be able to take others that are similar. Generally speaking, blood thinner drugs prevent blood clots from developing.